Security is an essential part of every organization, regardless of its size and the industry in which it operates. However, maintaining this security is difficult because the mode of attacks is continuously evolving and becoming more sophisticated. Also, an organization is likely to grow, thereby opening additional points of vulnerability.
One way to be on top of security and continuously identify and plug weak areas is through a comprehensive IT security audit. Additionally, these audits also meet the requirements of different cybersecurity standards, enabling organizations to become compliant with them.
What is IT Security Compliance?
IT Security Compliance, also called InfoSec, is the process of meeting the requirements set by relevant IT security standards. Since these standards are designed to protect an organization’s assets, following them is highly beneficial to organizations and safeguards them against likely attacks.
Why Audits are Essential for Risk Mitigation and Regulatory Adherence?
Regular audits allow you to check if all the standards’ requirements are being met. In case of any shortfall, you can take the necessary steps to meet them. As a result, audits help meet regulatory adherence and avoid the fines, penalties, and losses that can come with non-compliance. Moreover, when you meet these requirements, it reflects your commitment to security, and this enhances your reputation in the eyes of your customers, partners, employees, and other stakeholders.
Another advantage of audits is that they protect your organization from cyberattacks. When you identify vulnerabilities through audits, you can take the required action to fix them. In turn, this mitigates the risks that can come from possible attacks.
Due to these benefits, every organization must conduct regular audits for IT security compliance.
Now that you know the importance of audits, let us do a deep dive on what IT security compliance audit is, its process, and the standards it covers.
What Is an IT Security Compliance Audit?
An IT security compliance audit is an independent third-party review of your existing security practices, processes, and tools, intended to uncover vulnerabilities. This audit follows a series of established steps that certified auditors follow to evaluate the state of security in your organization and compare it with the requirements of standards.
Some common information security compliance standards are:
- ISO 27001 – A global standard for managing information security.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework – Largely used by U.S. federal agencies and contractors.
- HIPAA – U.S. law that sets standards for protecting health information.
- SOC 2 – Required by service providers and tech companies to prove that they are securely handling sensitive customer data.
- GDPR – The European law on data protection and privacy.
While the exact audit process depends on the size of your organization, the standards you follow, and the third-party auditors, here are the broad steps an IT security compliance audit covers.
- Evaluating existing policies for their effectiveness in maintaining your organization’s security.
- Doing a comprehensive inventory of IT assets.
- Performing a cybersecurity risk assessment to identify vulnerabilities.
- Evaluating existing access controls to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Remediating the identified risks.
- Creating an incident response plan and assigning responsibilities to individuals and teams for overseeing this plan’s implementation.
Next, let’s look into the areas that are covered by any IT compliance audit process.
Key Areas to Audit
A comprehensive IT security compliance audit will evaluate systems, processes, people, and tools to provide an accurate view of the IT security. If you’re an auditor or a team responsible for overseeing audits, below are the key areas to look into.
Network and Infrastructure Security
Network security compliance must be a core part of your audit because networks with vulnerabilities are quickly exploited by hackers. Make sure to check if the organization’s firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and firewalls are active and updated. Also, ensure that all security-related applications are patched with the latest updates. Overall, the goal here is to verify if the network ports are properly configured and the devices are monitored for unusual activity.
Access Controls and Identity Management
Who accesses what? This is a critical area that has a direct impact on the state of security in the network. Ideally, the organization must have robust access controls that allow only authorized users to access relevant information. It also helps if the organization has implemented an identity management system that will streamline access to resources.
Data Protection and Encryption
Data must be protected at all times, and the organization must have mechanisms to encrypt data while at rest and during transit. Such end-to-end encryption must be available at least for the sensitive data within the organization. Moreover, look into the kind of encryption used. It must be AES-256 or something similar. It also helps if the organization has a data classification system to continuously identify sensitive data and encrypt it automatically.
Incident Response Protocols
Though prevention mechanisms are key, the organization must also have an effective incident response plan, where employees know their responsibilities and actions in the event of a security incident. Incident logging, proper communication channels, and a review system are other areas to look into.
Logging and Monitoring Practices
The organization must have robust logging and monitoring practices that must be well-implemented. Check how logs are collected from servers, applications, etc, and are stored. The retention period and the security of these logs are other areas to look into. Using automated tools is a bonus as they can detect issues in real time.
Physical Security (if relevant)
Lastly, check the physical security, if relevant for the organization. There must be access controls for server rooms and data centers where critical information is stored. Similarly, the premise must have CCTV cameras, alarm systems, and a log of entry and exit.
After auditing these different areas, you can determine if an organization meets the required information security compliance standards.
The IT Compliance Audit Process: Step-by-Step
As discussed above, there are many key areas that must be looked into as part of the audit. To ensure that everything happens quickly and smoothly, you need a structured approach. Below is the step-by-step IT compliance audit process that can help you cover the above areas and identify any gaps that can impact the organization.
Define Audit Scope and Objectives
As a first step, set clear goals for your audit. For example, the goal can be to determine if the organization meets specific compliance standards like GDPR, SOC 2, etc. Similarly, work with the IT team to decide the scope. It can be specific systems, teams, or departments, or can encompass the entire organization.
Review Existing Documentation and Policies
Based on the scope, collect the required documentation, systems, policies, network diagrams, access controls, plans, and any other pertinent information that can help you perform the audit efficiently. While reviewing these assets, keep an eye on access controls, and make sure you have access only to what’s required for your scope of work.
Perform Technical Inspections and Vulnerability Scans
Use automated compliance tools and scanning software to identify problem areas like missing patches in applications, misconfigured systems, port vulnerabilities, outdated software, and faulty policy implementations. Perform vulnerability scanning and penetration testing to attack defense systems and identify weaknesses.
Interview Relevant Staff
Talk to IT admins, compliance officers, department heads, and other relevant staff to understand how policies are formulated and controls are implemented. Focus on the everyday monitoring and incident response plans to better understand the effectiveness of policies. This is a critical step as it can help identify vulnerabilities that often get missed in technical scans.
Analyze and Score Risks
One good way to determine the security state is to analyze each aspect and assign a score to it. Based on the criticality of the issue and its impact on the organization, you can rank the risks and encourage the organization to prioritize its resources accordingly.
Draft the Audit Report
Once you are done with identifying the shortcomings and assigning scores to them, put all your findings in an audit report. Back each finding or action item with relevant evidence for cross-reference. Use simple language, so everyone can understand the report well.
Recommend and Track Remediation Actions
Finally, include your recommendations on what the organization must do to improve its security posture. Provide a way to track remediation actions if you’re an external consultant, or if you’re an internal auditor, assign tasks to the relevant department or individuals, and track progress.
As you can see, manually auditing these different steps can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Also, there is always a possibility of errors. To avoid these issues, consider using IT audit software that comes with many features to do a deep scan, identify vulnerabilities in real-time, and pinpoint the cause of issues.
Benefits of Using IT Audit Software
IT audit software makes the audit process smooth and efficient, while making you more productive. Here are some key benefits of using these automated compliance tools.
- Reduce human errors.
- Gather data and analyze them in real time to identify vulnerabilities as they emerge.
- Speeds up effort-intensive tasks like data collection and log analysis. As a result, jobs that took days can be done in minutes.
- Built-in templates standardize reports and ensure you don’t miss the critical aspects in your report.
- Simplifies compliance for organizations that must meet different standards.
- Centralizes the storage of findings, so they can be used as evidence.
- Some tools track remediations.
- Most tools are scalable, and you can include more departments or areas as needed.
Undoubtedly, these benefits make your audits more effective for organizations. For a closer look at the different tools, check out our IT Security Audit Software Guide.
Top Tools to Support Your Audit
Selecting the right tool is key to an efficient and effective audit. Below are the top tools with many unique features to support every organization’s audit process.
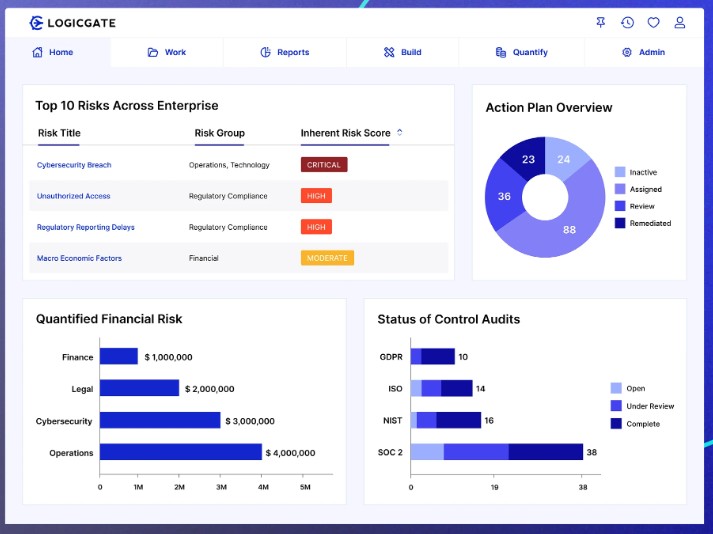
LogicGate
LogicGate’s Risk Cloud is a GRC platform that supports a wide range of standards, cyber risk controls, third-party risks, and more. Its key features are:
- Automates and quantifies risk programs for better effectiveness.
- Automates evidence collection to save time and effort.
- Adapts to your changing environment, making it relevant and scalable across many situations.
- Sends communication in multiple languages to reach different stakeholders.
Supported frameworks – GDPR, SCF, GLBA, SOC2, NIST, UCF, NIS 2, ISO, PCI-DSS, FedRAMP, CMMC, CCPA, HIPAA, Colorado privacy Act, and DORA.
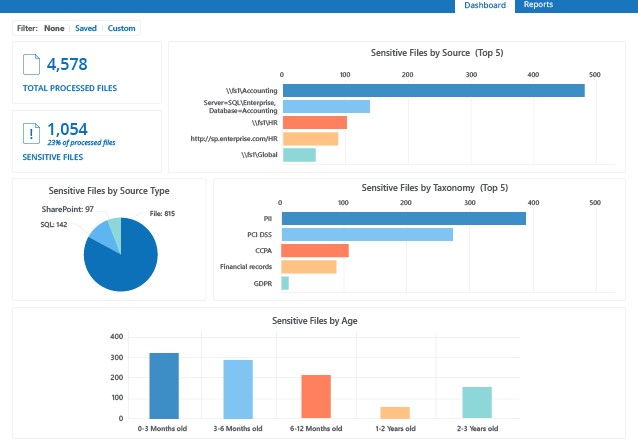
Netwrix
Netwrix Auditor is a comprehensive tool for external and internal security audits. It detects security threats quickly and helps optimize IT operations to meet compliance. Its key strengths are:
- Identifies the most pressing security gaps in data handling and infrastructure to minimize IT risks.
- Reduces audit preparation time by 85%, as per the website.
- Streamlines tasks to make the IT teams more productive.
- Creates a consolidated audit trail by integrating with popular platforms like Oracle, Microsoft, Nutanix, Dell, and more.
Supported frameworks – GDPR, NIST, ISO, PCI-DSS, CMMC, and HIPAA.
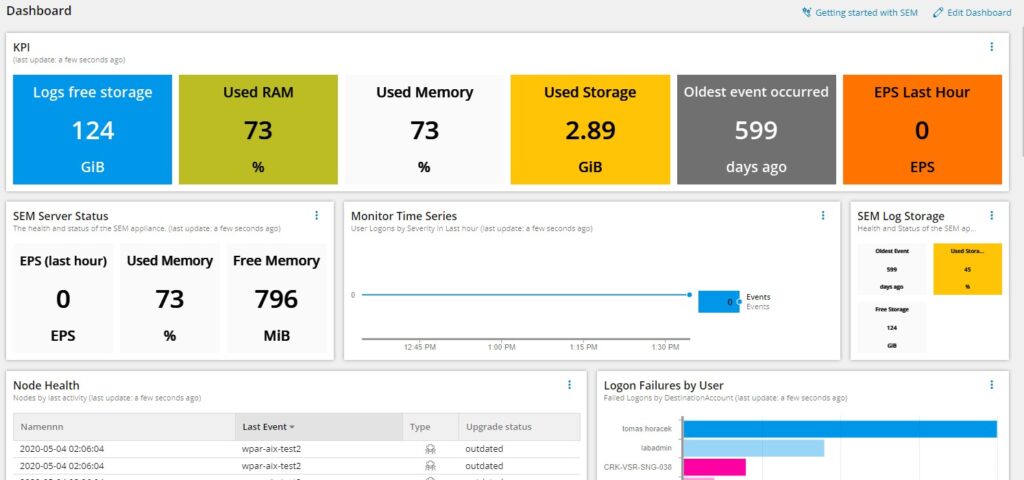
SolarWinds SEM
SolarWinds SEM automates monitoring to ensure your organization meets the required compliance standards. Below are the standout aspects of this tool.
- Centrally monitors log and event data for real-time detection and easy accessibility to supporting documents.
- Generates audit trails and compliance reports as mandated by many compliance standards.
- Provides an intuitive interface to log and respond to critical IT events.
- Offers comprehensive visibility into access controls, patch management, and more.
Supported frameworks – PCI DSS, GLBA, SOX, NERC CIP, and HIPAA.
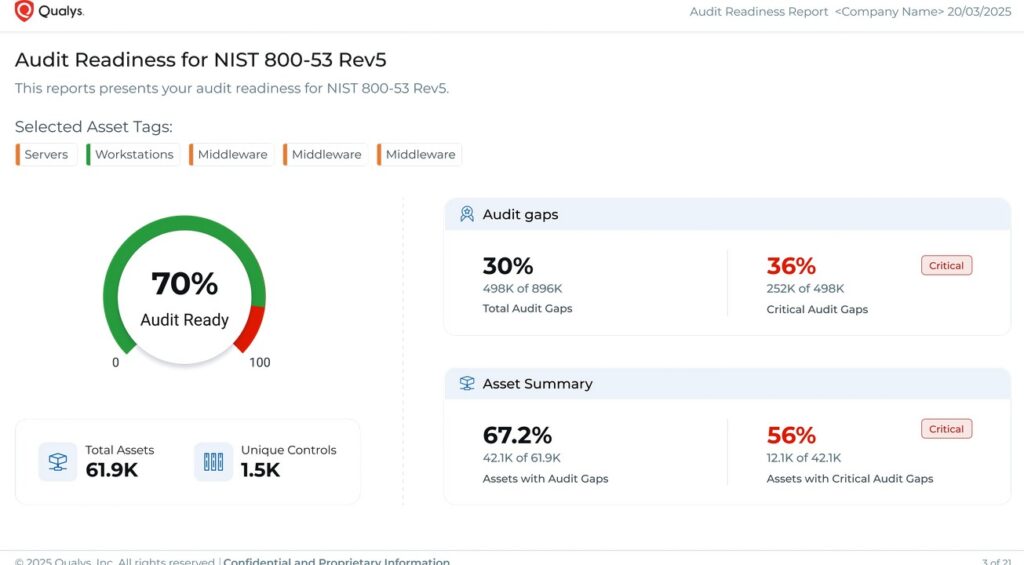
Qualys Policy Audit
Qualys Policy Audit is a next-gen platform that keeps your organization audit-ready always. Its continuous monitoring and automated remediation help you stay on top of existing and emerging risks. Additionally, it has the following strengths.
- Reduces audit preparation time by 75%, as per the website.
- Prioritizes compliance risks, so you can use your resources effectively to achieve compliance with different standards.
- Its pre-mapped controls help eliminate blind spots.
- Standardizes evidence collection to reduce audit-related errors.
Supported frameworks – NIS2, DORA, SOX, HIPAA, CoBIT
ManageEngine Log360
Log360 is a unified SIEM and SOAR solution that automates threat detection, investigation, and response. With a proactive approach, it streamlines audits and makes them highly effective. Other notable strengths of Log360 are:
- Detects issues across various log sources.
- Automatically identifies the sensitive data in your infrastructure.
- Points out misconfigurations and security gaps across devices and applications.
- Centralizes and manages logs for quick access.
- Automates incident management.
Supported frameworks – PCI-DSS 4.0, HIPAA, GDPR, SOX, CCPA, CPRA, GPG, FISMA, and CMMC.
As you can see, each of the above tools has unique capabilities to enhance the efficiency of your audits and improve the overall security posture of the organization. For a more detailed comparison, check out our IT security audit software guide.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Despite having the best tools, many organizations do not make the most of IT audits. A common problem with the inefficiency of these audits is poor or wrong scoping. When the scope is not defined properly, it creates chaos and eventually results in wasted resources and misalignment with regulatory requirements.
Another common problem is too much reliance on cybersecurity audit checklists without performing an in-depth analysis. While these checklists are helpful, they can create a false sense of completeness if not paired with expert judgment and contextual understanding.
Finally, the third common pitfall is the failure to follow up on remediation actions. Some organizations treat audits as a one-off exercise to achieve compliance and don’t take the necessary steps to improve their security. This results in failures in subsequent audits and can lead to financial loss.
Organizations that want to make the most of audits must steer away from these mistakes.
Final Words
To conclude, conducting regular audits is a proactive way to stay on top of security vulnerabilities and compliance gaps. With the right process and automated compliance tools, you can spot gaps and address them before they turn into big problems. Also, the tools discussed in this article can be reused for complying with multiple frameworks, and this saves time, effort, and costs.
To explore and compare these solutions in more detail, check out our IT security audit software guide. Taking the time to audit correctly today helps protect your business tomorrow.